KCCV 2015
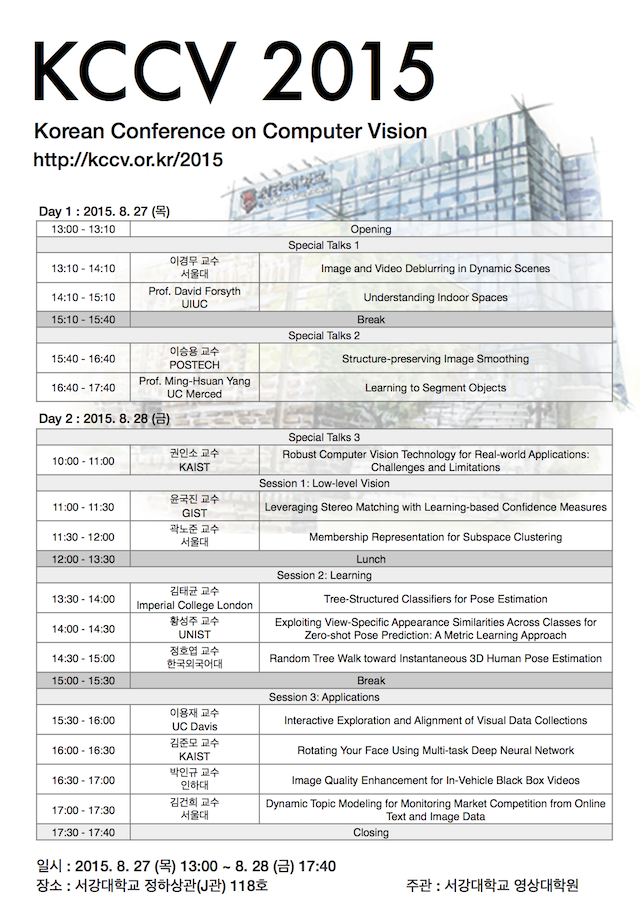
프로그램Day1 : 2015. 8. 27 (Thr)
Day2 : 2015. 8. 28 (Fri)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Image and Video Deblurring in Dynamic Scenes
연사: 이경무 교수 (서울대)
Abstract
In this talk, a novel image and video deblurring approaches will be introduced. Most state-of-the-art image/video deblurring methods are based on a strong assumption that the captured scenes are static. Thus, these methods often fail to deblur blurry images/videos in dynamic scenes. We propose locally adaptive image/video deblurring methods that can cope with general blurs inherent in dynamic scenes. To handle locally varying and general blurs caused by various sources, such as camera shake, moving objects, and depth variation in dynamic scenes, we employ a bidirectional optical flow model for the approximation of the pixel-wise blur kernel. Then, we formulate the problem as a single energy model that can estimates the optical flows and latent frames simultaneously. By minimizing the proposed energy function, we achieve significant improvements in removing blurs and estimating accurate optical flows in blurry frames. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art ones in real and challenging images and videos.
Biography
Kyoung Mu Lee received the B.S. and M.S. Degrees in Control and Instrumentation Eng. from Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea in 1984 and 1986, respectively, and Ph. D. degree in Electrical Engineering from the University of Southern California in 1993. He is currently with the Dept. of ECE at Seoul National University as a professor. His primary research interests include scene understanding, object recognition, MRF optimization, visual tracking, and visual navigation. He is currently serving as an AEIC (Associate Editor in Chief) of the IEEE TPAMI, an Area Editor of the Computer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU), and has served as an Associate Editor of the IEEE TPAMI, the Machine Vision Application (MVA) Journal and the IPSJ Transactions on Computer Vision and Applications (CVA), and the IEEE Signal Processing Letter. He also has served as a Program Chair of ACCV2012, a Track Chair of ICPR2012, Area Char of CVPR2012, CVPR2013, CVPR2015, ICCV2013, ECCV2014, and a Workshop Chair of ICCV2013. He was a Distinguished Lecturer of the Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association (APSIPA) for 2012-2013. More information can be found on his homepage http://cv.snu.ac.kr/kmlee .
Understanding indoor spaces
연사: Prof. David A. Forsyth (Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign)
Abstract
Rooms and indoor spaces are important, because humans live and work there. Robots built to help humans with day to day tasks, from cleaning to care of the frail, will need to work in rooms. There is now a rich literature studying methods to understand these indoor spaces from pictures and video. I will discuss methods to: model the overall shape of the space; identify important objects that are situated in the space; identify what people are doing, or could be doing, in the space; and investigate what the space would look like if objects were inserted or removed. My talk will provide a general review of methods and problems, with some particular application examples.
Biography
Structure-preserving Image Smoothing
연사: 이승용 교수 (POSTECH)
Abstract
Structure-preserving image smoothing is an essential operation with a variety of applications in computational photography and image analysis. Such an operation decomposes an image into prominent structure and fine-scale detail, making it easier for subsequent image manipulation such as tone mapping, detail enhancement, visual abstraction, scene understanding, and other tasks. In this talk, I will first review recent structure-preserving smoothing operators that can be classified into local filtering and optimization based solutions. I will then introduce novel structure-preserving image smoothing methods developed by POSTECH graphics group. The talk will be concluded with a few applications of structure-preserving image smoothing.
Biography
Seungyong Lee is a professor of computer science and engineering at the Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Korea. He received the BS degree in computer science and statistics from Seoul National University in 1988 and the MS and PhD degrees in computer science from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) in 1990 and 1995, respectively. From 1995 to 1996, he worked at the City College of New York as a postdoctoral researcher. Since 1996, he has been a faculty member of POSTECH, where he leads the Computer Graphics Group. During his sabbatical years, he worked at MPI Informatik (2003 2004) and the Creative Technologies Lab at Adobe Systems (2010 2011). His technologies on image deblurring and photo upright adjustment have been transferred to Adobe Creative Cloud and Adobe Photoshop Lightroom. His current research interests include image and video processing, non-photorealistic rendering, and 3D scene reconstruction.
Learning to Segment Object
연사: Prof. Ming-Hsuan Yang (Univ. of California, Merced)
Abstract
In this talk, I will present our recent work on learning to segment objects from exemplar images. First, we develop a method to generate object segmentation proposals from segmentation trees using exemplars. Compared to previous parametric methods, our data-driven method takes exploits rich content information from exemplars and thus generates a set of highly plausible proposals. Second, we propose novel random field models that enjoy joint learning of shape representation and object segmentation. Different from existing approaches that use shape representation as prior, our model emphasizes the structured prediction from the recognition model to the shape model. This difference ensures the shape is well preserved in the resulting segmentation masks with robustness to partial occlusions. Third, we develop a novel nonparametric method based on multiscale shape transfer, which in turns forms a higher-order random field. Compared to prior art that transfer rigid or deformable masks in image sub windows, our method explores shape masks in multiple granularities and is able to produce high quality segmentations in an efficient way. The last but not least, we develop a novel scene parsing system where small objects are segmented in context. With extensive use of context in multiscale and particular care to the long-tailed label distribution, our system demonstrates state-of-the-art results in large-scale problems.
Biography
Ming-Hsuan Yang is an associate professor in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at University of California, Merced. He received the PhD degree in Computer Science from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2000. He serves as an area chair for several conferences including IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, European Conference on Computer Vision, Asian Conference on Computer, AAAI National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, and IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition. He serves as a program co-chair and genera co-chair for Asian Conference on Computer Vision in 2014 and 2016. He serves as an associate editor of the IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2007 to 2011), International Journal of Computer Vision, Computer Vision and Image Understanding, Image and Vision Computing and Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research. Yang received the Google faculty award in 2009, and the Distinguished Early Career Research award from the UC Merced senate in 2011, the Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) award from the National Science Foundation in 2012, and the Distinguished Research Award from UC Merced Senate in 2015.
Robust Computer Vision Technology for Real-world Applications: Challenges and Limitations
연사: 권인소 교수 (KAIST)
Leveraging Stereo Matching with Learning-based Confidence Measures
연사: 윤국진 교수 (GIST)
Abstract
We propose a new approach to associate supervised learning-based confidence prediction with the stereo matching problem. First of all, we analyze the characteristics of various confidence measures in the regression forest framework to select effective confidence measures using training data. We then train regression forests again to predict the correctness (confidence) of a match by using selected confidence measures. In addition, we present a confidence-based matching cost modulation scheme based on the predicted correctness for improving the robustness and accuracy of various stereo matching algorithms. We apply the proposed scheme to the semi-global matching algorithm to make it robust under unexpected difficulties that can occur in outdoor environments. We verify the proposed confidence measure selection and cost modulation methods through extensive experimentation with various aspects using KITTI and challenging outdoor datasets.
Biography
Kuk-Jin Yoon is an associate professor in the School of Information and Communications at Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) in Korea. He received the B.S., M.S., and Ph.D. degrees in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) in 1998, 2000, 2006, respectively. He was a post-doctoral fellow in the PERCEPTION team at INRIA- Grenoble in France from 2006 and 2008 and joined the School of Information and Communications in Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Korea, as an assistant professor in 2008. He is currently a director of the Computer Vision Laboratory in GIST. His research interests are in general areas of computer vision and pattern recognition, including image-based 3D reconstruction, stereo matching, motion computing, visual tracking, and so on.
Membership representation for subspace clustering
연사: 곽노준 교수 (서울대학교)
Abstract
Recently, there have been many proposals with state-of-the-art results in subspace clustering that take advantages of the low-rank or sparse optimization techniques. These methods are based on self-expressive models, which have well-defined theoretical aspects. They produce matrices with (approximately) block-diagonal structure, which is then applied to spectral clustering. However, there is no definitive way to construct affinity matrices from these block-diagonal matrices and it is ambiguous how the performance will be affected by the construction method. In this talk, we propose an alternative approach to detect block-diagonal structures from these matrices. The proposed method shares the philosophy of the above subspace clustering methods, in that it is a self-expressive system based on a Hadamard product of a membership matrix. To resolve the difficulty in handling the membership matrix, we solve the convex relaxation of the problem and then transform the representation to a doubly stochastic matrix, which is closely related to spectral clustering. The result of our method has eigenvalues normalized in between zero and one, which is more reliable to estimate the number of clusters and to perform spectral clustering. The proposed method shows competitive results in our experiments, even though we simply count the number of eigenvalues larger than a certain threshold to find the number of clusters.
Biography
Nojun Kwak was born in Seoul, Korea in 1974. He received the BS, MS, and PhD degrees from the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, in 1997, 1999 and 2003 respectively. From 2003 to 2006, he was with Samsung Electronics. In 2006, he joined Seoul National University as a BK21 Assistant Professor. From 2007 to 2013, he was a Faculty Member of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea. Since 2013, he has been with the Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, where he is currently an Associate Professor. His current research interests include pattern recognition, machine learning, computer vision, data mining, imageprocessing, and their applications.
Tree-Structured Classifiers for Pose Estimation
연사: 김태균 교수 (Imperial College London)
Abstract
Many computer vision tasks can be cast as large-scale classification problems, where extremely efficient and powerful classification methods are pursued. Boosting with decision stump learners, the state-of-the-art for objet detection, can be seen as a flat structure, while many developments including a Boosting cascade can be seen as a deeper tree structure. Randomised Decision Forests is an emerging technique in the fields. A hierarchical structure yields many short paths, accelerating evaluation time, while feature randomisation promotes good generalisation to unseen data. It is inherently for multi-class classification problems. In this talk, we see applications of Randomised Decision Forests and tree-structured methods with comparisons and insights. The talk focuses on articulated hand pose estimation, and 6DOF object pose estimation. Hands are highly articulated and deformable objects, playing a key role for novel man-machine interfaces. Estimating their 3D postures, or regressing locations of joints is highly challenging. We have tackled the problems by various novel ideas on top of the cutting-edge techniques. We conclude the talk with some future directions including active interactive object recognition. More information is found at http:www.iis.ee.ic.ac.uk/ComputerVision.
Biography
Tae-Kyun Kim is an Assistant Professor in computer vision and learning at Imperial College London, UK, since 2010. He obtained his PhD from Univ. of Cambridge in 2008 and had been a Junior Research Fellow (governing body) of Sidney Sussex College, Univ. of Cambridge during 2007-2010. His research interest spans various topics including: hand gesture recognition, object recognition, detection and 6DOF pose estimation, active robot vision, multiple object tracking, face analysis and recognition, activity recognition, and novel man-machine interface. He has co-authored over 40 academic papers in top-tier conferences and journals in the field, 6 MPEG7 standard documents and 17 international patents. His co-authored algorithm is an international standard of MPEG-7 ISO/IEC for face image retrieval.
Exploiting View-Specific Appearance Similarities Across Classes for Zero-shot Pose Prediction: A Metric Learning Approach
연사: 황성주 교수 (UNIST)
Abstract
Viewpoint estimation, especially in case of multiple object classes remains an important and very challenging problem. First, objects under different views undergo extreme appearance variations, often making within-class variance larger than between-class variance. Second, obtaining precise ground truth for real-world images, necessary for training supervised viewpoint estimation models, is extremely difficult and time consuming. As a result, annotated data is often available only for a limited number of classes. Hence it is desirable to share viewpoint information across classes, but it is difficult to define viewpoint alignment across classes in practice. To address these problems, we propose a metric learning approach for joint class prediction and pose estimation. Our metric learning approach allows us to circumvent the problem of viewpoint alignment across multiple classes, and does not require precise or dense viewpoint labels. Moreover, we show, that the learned metric generalises to new classes, for which the pose labels are not available, and therefore makes it possible to use only partially annotated training sets, relying on the intrinsic similarities in % structures of the viewpoint manifolds. We evaluate our approach on two challenging multi-class datasets, 3DObjects and PASCAL3D+.
Biography
Random Tree Walk toward Instantaneous 3D Human Pose Estimation
연사: 정호엽 교수 (한국외국어대학교)
Abstract
The availability of accurate depth cameras have made real-time human pose estimation possible; however, there are still demands for faster algorithms on low power processors. This paper introduces 1000 frames per second pose estimation method on a single core CPU. A large computation gain is achieved by random walk sub-sampling. Instead of training trees for pixel-wise classification, a regression tree is trained to estimate the probability distribution to the direction toward the particular joint, relative to the current position. At test time, the direction for the random walk is randomly chosen from a set of representative directions. The new position is found by a constant step toward the direction, and the distribution for next direction is found at the new position. The continual random walk through 3D space will eventually produce an expectation of step positions, which we estimate as the joint position. A regression tree is built separately for each joint. The number of random walk steps can be assigned for each joint so that the computation time is consistent regardless of the size of body segmentation. The experiments show that even with large computation gain, the accuracy is higher or comparable to the state-of-the-art pose estimation methods.
Biography
Ho Yub Jung received the B.S. electrical engineering from University of Texas at Austin in 2002 and the M.S. and Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering and computer science from the Seoul National University in 2006 and 2012.. During 2012 to 2014, he was with Samsung Electronics, in the Digital Media and Communications R&D Center. From 2014, he is currently a faculty member at Division of Computer and Electronics System Engineering in Hankuk University of Foreign Studies. His research interests include computer vision, human pose estimation, machine learning, and medical imaging.
Interactive Exploration and Alignment of Visual Data Collections
연사: 이용재 교수 (UC-Davis)
Abstract
In this talk, I will present an interactive framework that allows a user to rapidly explore and visualize a large image collection using the medium of average images. Average images have been gaining popularity as means of artistic expression and data visualization, but the creation of compelling examples is a surprisingly laborious and manual process. Our interactive, real-time system provides a way to summarize large amounts of visual data by weighted average(s) of an image collection, with the weights reflecting user-indicated importance. The aim is to capture not just the mean of the distribution, but a set of modes discovered via interactive exploration. We pose this exploration in terms of a user interactively “editing” the average image using various types of strokes, brushes and warps, similar to a normal image editor, with each user interaction providing a new constraint to update the average. New weighted averages can be spawned and edited either individually or jointly. Together, these tools allow the user to simultaneously perform two fundamental operations on visual data: user-guided clustering and user-guided alignment, within the same framework. We show that our system is useful for various computer vision and graphics applications.
Biography
Yong Jae Lee is an Assistant Professor in the CS Department at UC Davis, as of Fall 2014. Prior to that, he spent a year in the EECS Department at UC Berkeley and a year in the Robotics Institute at Carnegie Mellon University as a Postdoctoral Fellow. He received his Ph.D. from the University of Texas at Austin in 2012, and his B.S. from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2006. His research interests are in computer vision, machine learning, and computer graphics.
Rotating Your Face Using Multi-task Deep Neural Network
연사: 김준모 교수 (KAIST)
Abstract
Face recognition under viewpoint and illumination changes is a difficult problem, so many researchers have tried to solve this problem by producing the pose- and illumination- invariant feature. Zhu et al. changed all arbitrary pose and illumination images to the frontal view image to use for the invariant feature. In this scheme, preserving identity while rotating pose image is a crucial issue. In this talk, we propose a new deep architecture based on a novel type of multitask learning, which can achieve superior performance in rotating to a target-pose face image from an arbitrary pose and illumination image while preserving identity. The target pose can be controlled by the user’s intention. This novel type of multi-task model significantly improves identity preservation over the single task model. By using all the synthesized controlled pose images, called Controlled Pose Image (CPI), for the pose-illumination- invariant feature and voting among the multiple face recognition results, we clearly outperform the state-of-the-art algorithms by more than 4 6% on the MultiPIE dataset.
Biography
Junmo Kim (S’01-M’05) received the B.S. degree from Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, in 1998, and the M.S. and Ph.D. degrees from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, in 2000 and 2005, respectively. From 2005 to 2009, he was with the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT), Korea, as a Research Staff Member. He joined the faculty of KAIST in 2009, where he is currently an Assistant Professor of electrical engineering. His research interests are in image processing, computer vision, statistical signal processing, and information theory.
Image Quality Enhancement for In-Vehicle Black Box Videos
연사: 박인규 교수 (인하대학교)
Abstract
In-vehicle black box camera (dashboard camera) has become a popular device for security monitoring and event capturing. In this talk, I address two problems to improve the quality of captured videos of black box cameras. (1) Black box videos have difficulty in maintaining consistent intensity and color tone from frame to frame. Particularly, it happens when the black box camera has to deal with fast changing illumination environment. To handle this problem properly, we introduce a novel tone stabilization method to enhance the performance of further applied algorithms like detecting and matching visual features across video frames. The proposed technique utilizes multiple anchor frames as references to smooth tone fluctuation between them. (2) The readability of video content is often degraded due to the windscreen reflection of objects inside. We propose a novel method to remove the reflection on the windscreen. The method exploits the spatio-temporal coherence of reflection, which states that a vehicle is moving fast forward while the reflection of the internal objects remains static. The average image prior is proposed by imposing a heavy-tail distribution with a higher peak to remove the reflection. A non-convex cost function is developed and optimized fast in a half quadratic
Biography
In Kyu Park received his BS, MS, and PhD degrees from Seoul National University in 1995, 1997, and 2001, respectively, all in electrical engineering and computer science. From September 2001 to March 2004, he was with Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT). Since March 2004, he has been with the Department of Information and Communication Engineering, Inha University, where he is currently an associate professor. From January 2007 to February 2008, he was an exchange scholar at Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL). From September 2014 to August 2015, he was a visiting associate professor at MIT Media Lab. His research interests include computer vision, computational photography, and GPGPU. He is a Senior Member of IEEE and a member of ACM.
Dynamic Topic Modeling for Monitoring Market Competition from Online Text and Image Data
연사: 김건희 교수 (서울대학교)
Abstract
We propose a dynamic topic model for monitoring temporal evolution of market competition by jointly leveraging tweets and their associated images. For a market of interest (e.g. luxury goods), we aim at automatically detecting the latent topics (e.g. bags, clothes, luxurious) that are competitively shared by multiple brands (e.g. Burberry, Prada, and Chanel), and tracking temporal evolution of the brands’ stakes over the shared topics. One of key applications of our work is social media monitoring that can provide companies with temporal summaries of highly overlapped or discriminative topics with their major competitors. We design our model to correctly address three major challenges: multi-view representation of text and images, modeling of competitiveness of multiple brands over shared topics, and tracking their temporal evolution. As far as we know, no previous model can satisfy all the three challenges. For evaluation, we analyze about 10 millions of tweets and 8 millions of associated images of the 23 brands in the two categories of luxury and beer. Through experiments, we show that the proposed approach is more successful than other candidate methods for the topic modeling of competition. We also quantitatively demonstrate the generalization power of the proposed method for three prediction tasks.
Biography
Gunhee Kim is an assistant professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering of Seoul National University from 2015. Prior to that, he was a postdoctoral researcher at Disney Research for one and a half years. He received his PhD in 2013 under Eric P. Xing from Computer Science Department of Carnegie Mellon University. Prior to starting PhD study in 2009, he earned a master’s degree under supervision of Martial Hebert in Robotics Institute, CMU. His research interests are solving computer vision and web mining problems that emerge from big image data shared online, by developing scalable and effective machine learning and optimization techniques. He is a recipient of 2014 ACM SIGKDD doctoral dissertation award.
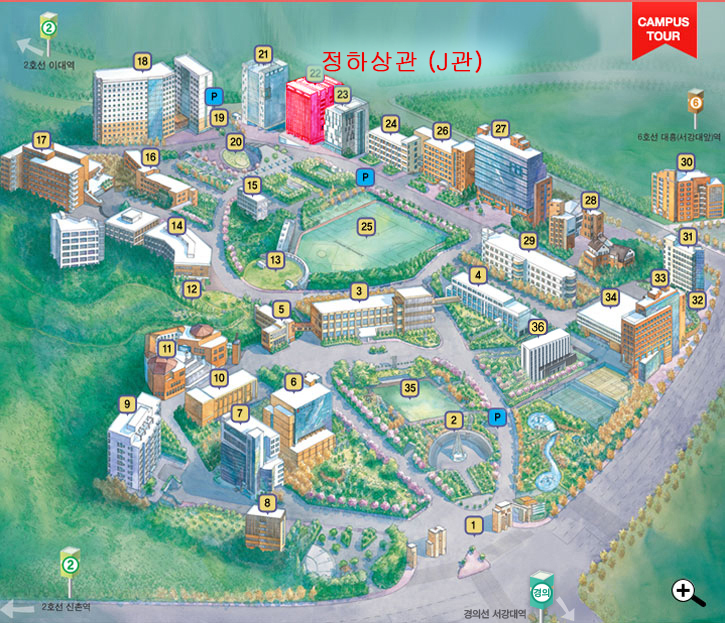
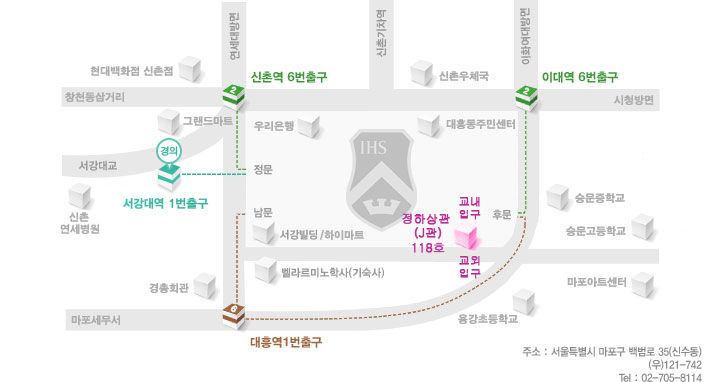
장소 안내
약도 및 교통안내대중교통 : http://sogang.ac.kr/intro/campus/c_roughmap.html 주차 : 주차 할인권을 제공합니다. 그러나 행사장 주변의 교통이 복잡하오니 대중교통 이용을 권장합니다.
|
등록 안내사전 등록 : 2015. 07. 27. (Mon) - 08. 21. (Fri) [ 등록 사이트 ]
현장 등록 : 2015. 08. 27. (Thr) 12:00 - 08. 28 (Fri) 15:00
점심식사 : 28일 구내식당 식권제공 주차 : 주차 할인권을 제공합니다. 그러나 행사장 주변의 교통이 복잡하오니 대중교통 이용을 권장합니다.
|